Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen Therapy
The benefits of oxygen therapy for various medical conditions, such as COPD, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis.
To know the benefits of oxygen therapy, we must know that it is a treatment that involves breathing in higher concentrations of oxygen than are typically present in the air we breathe. It is used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and chronic bronchitis.
For people with COPD, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis, the benefits of oxygen therapy can help to:
- Increase the amount of oxygen in the blood, which can help the body’s organs and tissues function better
- Reduce shortness of breath
- Improve exercise tolerance
- Delay the progression of the disease
- Improve quality of life
- Reduce the risk of hospitalization and death.
Oxygen therapy is usually administered through a device called an oxygen concentrator, which is a machine that separates oxygen from other gases in the air and delivers it to the patient via a nasal cannula or mask. In some cases, liquid oxygen or compressed oxygen in tanks may also be used. But the best and Modern device are the POC (Portable Oxygen Concentrator)
It’s important to note that Oxygen therapy is a prescription based treatment, the person’s blood oxygen level is measured, and the therapy is prescribed based on the result. Oxygen therapy should be under the guidance of a trained medical professional.
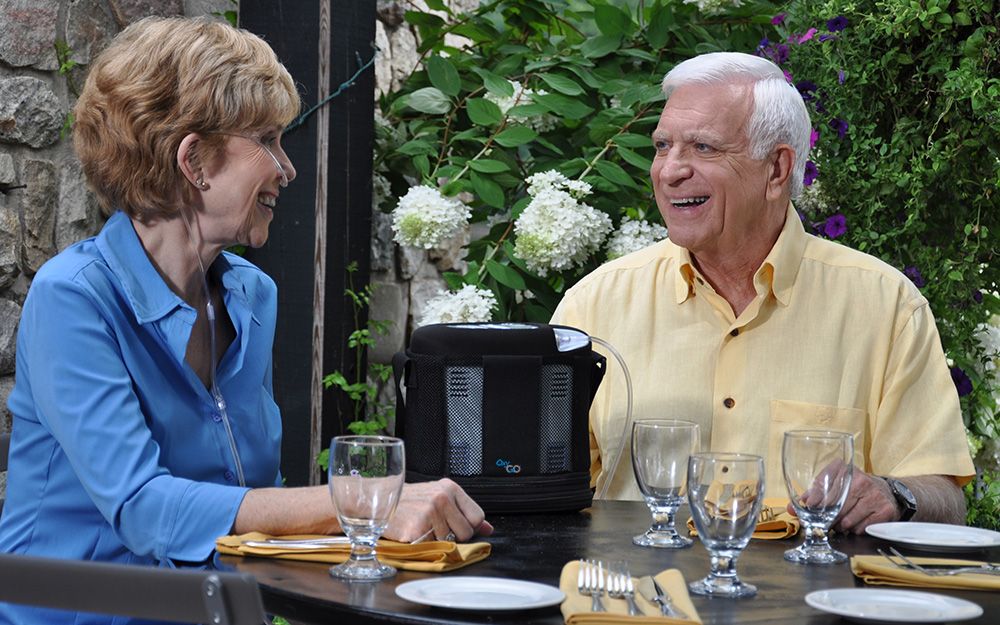

If you are being treated with oxygen therapy you should know about POCs
Portable oxygen concentrators (POCs) are a type of oxygen therapy equipment that are small, lightweight, and battery-powered, which makes them easy to carry around. They work by extracting oxygen from the air and delivering it to the person through a nasal cannula or mask. POCs can be used both at home and on the go, which makes them a convenient option for people who need oxygen therapy.
There are several advantages of using POCs over other types of portable oxygen, such as tanks or cylinders:
- They are more compact and lightweight, making them easy to carry around with you, whether you’re at home, out running errands, or traveling.
- They are self-contained and don’t need to be refilled, which means that you don’t have to worry about running out of oxygen when you’re away from home.
- They are typically more energy-efficient and have a longer battery life than tanks or cylinders.
- They are much more environmentally friendly since they do not use tanks which has to be disposed of.
- They can run on electrical power or batteries, which allows you to use them even when you don’t have access to a power outlet.
That being said, POCs are not the best option for everyone who needs oxygen therapy. If a person requires a high-flow of oxygen, POCs may not be able to deliver the required amount. Also, POCs are not as durable as other types of equipment, so they may be more susceptible to damage from wear and tear. In those cases, other options such as liquid or compressed oxygen tanks or a home-based concentrator may be more appropriate.
A physician or a respiratory therapist is the best person to make the decision with the patient if a POC is the best option for the patient based on the patient’s specific needs and lifestyle.
The different types of oxygen therapy available, such as continuous, intermittent, and pulse flow, and how to choose the best option for you.
There are several different types of oxygen therapy that can be used to treat conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung disorders that cause difficulty breathing. The main types of oxygen therapy include:
- Continuous flow: This type of oxygen therapy provides a steady stream of oxygen to the patient, 24 hours a day. It is typically used for patients with severe lung disorders who require a high oxygen concentration at all times.
- Intermittent flow: This type of oxygen therapy provides oxygen to the patient only when they inhale. It is typically used for patients with less severe lung disorders who do not require a constant oxygen supply.
- Pulse flow: This type of oxygen therapy delivers a burst of oxygen with each breath the patient takes. It is used in patients with COPD who have a high level of exertion and require increased oxygen flow during activities.
The best option for you will depend on the specific condition you have and how severe it is, as well as your lifestyle and level of activity. Your doctor will be able to evaluate your needs and recommend the best type of oxygen therapy for you.



Oxygen therapy in COVID 19
Oxygen therapy is a common treatment for individuals with COVID-19, especially those with severe or critical illness. The virus can cause inflammation in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing and low oxygen levels in the blood. Oxygen therapy can help to supplement the oxygen needs of the body, potentially preventing or delaying the need for mechanical ventilation. It can be administered through a variety of methods, including through a nasal cannula or a mask, and can be given in a hospital setting or at home.
Oxygen therapy is a essential therapy for covid patients and in most of the cases it’s the first line therapy. It helps in preventing serious deterioration in the condition of the patient and in many cases avoiding intubation or mechanical ventilation.
It’s important to note that for some patients the oxygen therapy alone may not be sufficient and may require other therapies as well.
 Español
Español
